Knee Replacement - Treatment
Non-operative Treatment
Conservative treatment options are always tried first. These include:
- activity modification.
- exercise and conditioning.
- anti-inflamatory medication.
- Physical therapy programs in water (aquatic therapy) allow patients to exercise in non-weightbearing situations.
- Shock-absorbing shoe inserts often relieve some pain during activities.
- The injection into the joint of either cortisone or newer visco supplements such as hyaluronic acid may provide temporary relief for moderate to severe conditions.
- neoprene sleeves and other dynamic braces to correct mal-alignment of the leg.
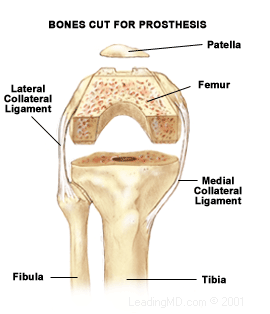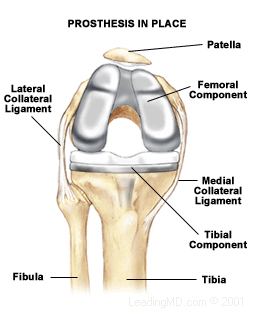
Operative Treatment
Patients having night pain, difficulty walking or performing normal activities may be candidates for surgery. Operative treatments may include:
- arthroscopy and debridement (removal) of loose chondral fragments in the joint lining if the patient has symptoms such as pain and swelling.
- osteotomy, which corrects the mal-alignment of the lower leg.
- Finally, knee replacement surgery may dramatically relieve the symptoms of knee arthritis.
Total Knee Replacement
Total knee replacement is an option for the patient who has not improved after trying the conservative measures described above and whose quality of life is severely affected. In knee replacement surgery all diseased cartilage is removed, and a metal and plastic prosthesis or replacement, is inserted. It is attached to the bone with bone cement or ingrowth of bone into the prothesis. The surgery takes one to two hours and requires a three to five day hospital stay. The results of knee replacement surgery are reliable, and over 95% of patients report good to excellent results at ten years.
BackNext